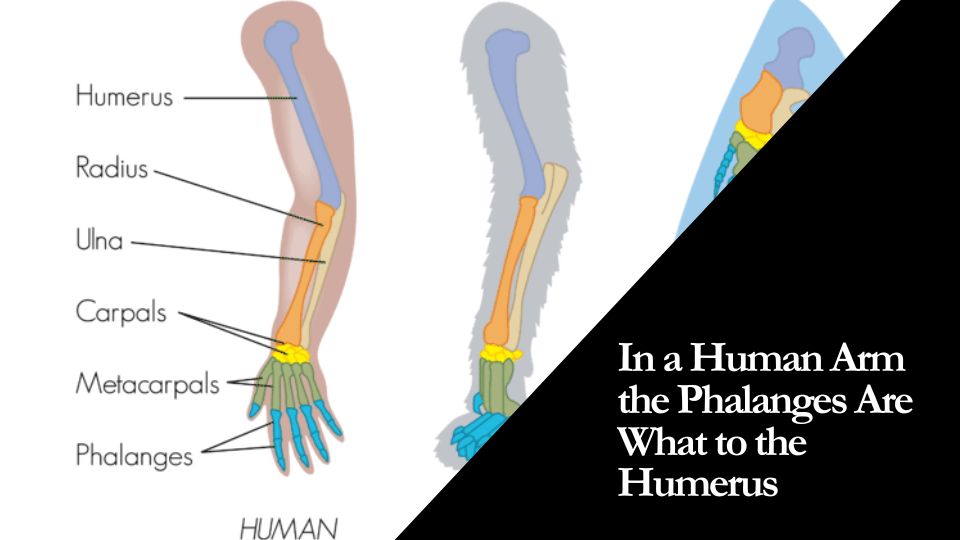
The human arm, an amazing feat of biological engineering, constitutes several complex structures including bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves. Among these, bones are the essential supporting framework, of which the humerus, radius, ulna, and phalanges are key constituents. Understanding the importance of these bones, mainly the phalanges and humerus, is crucial for a deeper insight into the human skeletal system.
What Are the Phalanges?
In the broad anatomical panorama, the phalanges are the finger bones located in the hand. Each finger comprises three types of phalanges: the proximal phalanx, the middle phalanx, and the distal phalanx, all surrounded by various tendons, ligaments, and muscles to facilitate movement and strength.
Proximal Phalanx
The proximal phalanx, the first bone in each finger, attaches to the metacarpals of the hand. The joint where both connect is enveloped by synovial fluid, ensuring smooth movements and preventing bone degradation.
Middle Phalanx
The middle phalanx, the second bone, connects the proximal and distal phalanx. Surrounded by cartilage and ligaments, it enables our fingers to flex and extend.
Distal Phalanx
The distal phalanx is the last bone, ending at the fingertips. The fingernails anchor themselves to this bone, and it provides the hand with fine motor control skills, crucially impacted by the nervous system.
What Is the Humerus?
The humerus, a long bone in the upper arm, extends from the shoulder to the elbow, connecting to the radius and ulna. The completeness of the muscular system is seen here, enabling various arm and elbow movements.
Anatomy of the Humerus
The humerus, encapsulated by skin, harbours arteries, veins, capillaries, and lymphatic vessels – integral parts of the circulatory system and lymphatic system. It is rich in nerve supply from spinal and peripheral nerves, enabling both sensory and autonomic responses.
Functions of the Humerus
The humerus facilitates arm movement, providing strength and stability. It functions as a site for muscle attachment, contributing to the functional integrity of the muscular and skeletal systems.
How Do the Phalanges and the Humerus Work Together?
The synchronized functioning of phalanges and the humerus ensures optimal hand and arm performance.
Movement of the Fingers
The interplay between phalanges, humerus, and muscles grant us an impressive range of finger movements, including fine motor skills like writing or playing an instrument. The efficient nerve transmissions via cranial and spinal routes allow this.
Stability of the Arm
The humerus’s length and robustness provide stability to the arm, assisted by muscles and tendons. The hand’s capability to grasp and manipulate objects owes this to the strategic location and function of phalanges.
How Can the Phalanges and the Humerus Be Injured?
Injuries to the phalanges and humerus are common due to their extensive usage and exposure.
Common Phalanges Injuries
Fractures, dislocations, and sprains are common in phalanges. They often result from falls, sports injuries, or work-related traumas, and immediate medical attention is crucial.
Common Humerus Injuries
Humerus fractures or dislocations can limit arm mobility. They typically result from high-impact trauma or conditions like osteoporosis.
How to Take Care of Your Phalanges and Humerus
Taking care of these bones helps maintain the functional integrity of the arm as well as overall body health, involving a mix of exercises, nutrition, and a balanced lifestyle.
Exercises for the Fingers
Regular finger exercises strengthen muscles, increase joint flexibility, and improve circulation.
Exercises for the Arm
Arm exercises specifically target arm muscles, enhancing endurance, strength, and performance.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Healthy dietary habits aid in maintaining overall bone health. Adequate vitamin D and calcium intake, along with regular exercise, play a pivotal role. A regular check-up can also help prevent potential issues and ensure optimal functioning of not only the circulatory system but also the immune system, endocrine system, reproductive system, digestive system, respiratory system, nervous system, excretory system, and integumentary system.
Conclusion
Both the phalanges and the humerus play significant roles in the human arm, contributing to its myriad capabilities – from gross motor movements to delicate, fine-tuned skills. The phalanges, making up our fingers, are instrumental in precise hand movements while the humerus provides structural stability and mobility to the arm. When these bones work in harmony, they afford us the extensive range of motions we often take for granted.
Injuries to these vital structures may detrimentally impact our day-to-day functioning. Therefore, ensuring their wellbeing through regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet replete with nutrients essential for bone health, and a lifestyle that minimizes the risk of injuries, should be actively pursued.
The human body, a marvel of evolution, functions through an intricate network of systems: from the immune system, protecting us from diseases; the endocrine system, regulating our metabolism and mood; the reproductive system, continuing the miracle of life; the digestive system, ensuring we derive nutrients from our food; the respiratory system, providing the life-sustaining oxygen; the circulatory system, distributing essential nutrients and oxygen throughout our body; the nervous system, coordinating responses and actions; the skeletal system, providing structural support; the muscular system, aiding locomotion; the excretory system, disposing off waste; to the integumentary system, offering protection.

Welcome to our blog! My name is Yuvraj Kore, and I am a blogger who has been exploring the world of blogging since 2017. It all started back in 2014 when I attended a digital marketing program at college and learned about the intriguing world of blogging.